1) Definition of sensor: An apparatus or device that is capable of sensing a specified signal under test that can be converted into an available output signal as per a certain rule, usually consisting of a sensitive component and a conversion component.
2)Linearity (non-linear error): Degree of linearity between the output and input of the sensor.

δL: Linearity (non-linear error); Δmax: Maximum non-linear absolute error; yF.S: Output full scale.
3) Sensitivity: Ratio of the output change to the input change of the sensor in steady state.

4) Lag: Lag or hysteresis refers to the degree of misalignment of the forward and reverse stroke outputs when the measurement at full measurement range is performed under the same operating conditions. The magnitude of lag is expressed as the percentage of the maximum deviation ΔHmax between the forward and the reverse stroke outputs of the same input amount when it is calibrated in the full scale to the output at the full scale.
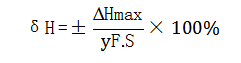
5) Repeatability: Degree of inconsistency of the characteristic curves of the sensor when the input amount is continuously changed in many times in the full scale at the same direction. Generally, the repeatability index is expressed as a percentage of the maximum non-repetitive output error Δmax and the full-scale output yF.S.
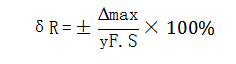
6) Resolution: An ability that describes that a sensor can sense the minimum change of the volume under test. Generally, the range of resolution of each input point is different. The maximum resolvable range of the input that changes the output step in full scale is used as a measurable indicator, which is defined as the resolution (Δmax) of the sensor. It also may be expressed in resolution, namely accuracy.
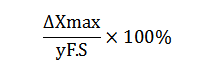
7)Accuracy: Degree of reliability of a measurement, which indicates the ability to repeat a reading with a given accuracy. The smaller the error, the higher the accuracy of the sensor. The accuracy of the sensor is expressed as a percentage of the maximum basic error over its scale to the full scale.
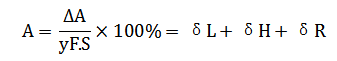
ΔA: Maximum basic error allowed within the measurement range.
Dynamic Characteristics: Response characteristics of the sensor to the input signal x (t) that varies with time.
9)Response Rate: The frequency response usually refers to the change of the impedance of the system or metering sensor with frequency;
10)Frequency Response: Within the specified frequency range of the volume under test, for the sine volume under test applied on the sensor, it refers to the change of the ratio of amplitude of the output to that of the volume under test and the difference between the output and the volume under test with the frequency. Note: The frequency response should be based on the frequency within the specified frequency range of the volume under test and a specified volume under test.
11)Orthogonality: Perpendicularity between the three mutually perpendicular measuring axes following the right-hand rule and the vertical positioning surface;
12)Power Consumption: The maximum power wattage that the sensor consumes within the operating range under steady-state conditions.
13) Reliability: Possibility (probability) that the sensor operates properly under the specified conditions. Specified Conditions: Specified time, environmental conditions, maintenance conditions, and use conditions of products.
14)Operating Temperature Range: Ambient temperature range under which the sensor can function normally;
15)Operating Humidity Range: Ambient humidity range under which the sensor can function normally;
16) Shock Resistance: Vibration limit that the magnetic sensor can withstand during normal operation;
17) Service Life: The shortest time that the sensor applies the specified continuous and intermittent rated values without changing its performance.
18)Surge Current: Peak current generated when a power source is turned on;
19)Anti-power Reverse: A protection measure to prevent power back connection;
20)Signal Output Protection: Protection for signal output over-limit;
21)Electromagnetic Compatibility (EMC): An ability of a device or system operating in its electromagnetic environment in line with the requirements, without causing unacceptable electromagnetic disturbances to any device in its environment;