Geophysics uses physics theories and methods to study the internal structure, construction and dynamic process of the earth, including potential field theory and wave theory. The potential field theory includes the Earth's gravity field, magnetic field, temperature field, natural electric field and DC electric field. The corresponding branches of science include gravity survey, magnetic survey, terrestrial heat flow survey and electric survey. Wave theories include acoustic theory, seismic wave theory and electromagnetic wave theory. The branches of science include water depth survey, seismic survey and electromagnetic survey.
1)Geomagnetic field
The general geomagnetic field can only be regarded as the surface magnetic field of the earth, not the global magnetic field of the earth (also called the space magnetic field), which is formed by the rotation of the earth's core. The internal structure of the earth includes the earth's crust, mantle and core. The earth's magnetic field is of dipole. It is similar to a shape of a magnetic field that a magnet rod is put in the center of the earth, making its N pole substantially opposite the South Pole. Actually, there is no magnet rod in the center of the earth. The generally accepted theory is that a magnetic field is generated by the generator effect of current flowing in the core of the conductive liquid.
It is found by American scientists in the experiments that the rotation speeds inside and outside the earth is different, and the rotation speed of the earth's core is greater than that of the earth's crust. In other words, although the people on the surface of the earth feel no rotation of the earth, but can feel the mass field effect generated by the rotation of the earth's core, that is, it generates the surface magnetic field of the earth. It is also found by the scientists in studies that the rotation axis of the earth's core is not aligned with that of the earth. Therefore, the two poles of the geomagnetic field formed by the rotation of the earth's core do not coincide with the geographical poles. This is the reason for the magnetic declination angle of the geomagnetic field.
It is found by the scientists in studies on the geomagnetic field that the geomagnetic field is changing, not only its intensity is not constant and the magnetic pole is changing; the magnetic reversal occurs at intervals. The geomagnetic field is affected by external disturbances, rather than isolated; the spacecraft has already detected the presence of solar wind. The solar wind is a high-temperature, high-speed, low-density particle flow ejected from the solar corona to the interplanetary space, and its main components are ionized hydrogen and ionized helium.
Because the solar wind is plasma, it also has a magnetic field. The magnetic field exerts an effect on the earth's magnetic field, as if the earth's magnetic field is blown away from the earth. However, the earth's magnetic field still effectively prevents the flood of solar wind. Under the resistance of the geomagnetic field, the solar wind bypasses the geomagnetic field and continues to move forward, forming a comet-like geomagnetic field surrounded by the solar wind. This is the magnetosphere.
The earth's magnetosphere is located at a height of 600-1,000 km from the ground. Its outer boundary is called the magnetopause, which is located at 50,000km-70,000 km from the ground. Under the compression of the solar wind, the earth's magnetic line extends far away from the space back to the side of the sun, forming a long tail called the magnetotail. There is a special interface near the magnetic equator. On both sides of the interface, the magnetic line suddenly changes its direction. This interface is called the neutral sheet. The intensity of the magnetic field on the neutral sheet is very little with the thickness of about 1,000km. The neutral sheet divides the magnetotail into two parts: the magnetic line on the north faces the earth, and the magnetic line on the south leaves the earth.
The geomagnetic field is one of the physical properties of the earth. It is the existence of an objective distribution of spatial quality and quantity. The geomagnetic field is a vector field, which directly affects the kinematics of all charged and magnetic objects in the earth system, and provides a natural coordinate system for all dynamic and static objects on the earth. The geomagnetic field is a stable and reliable natural resource, the geomagnetic resources is public, and the geomagnetic vector at each point on the earth is uniquely determined. In a Cartesian coordinate system, there are 7 geomagnetic elements: magnetic declination angle D, magnetic dip angle I, total geomagnetic field intensity T, vertical geomagnetic field intensity Z, horizontal magnetic field intensity H (including horizontal X component (north), and horizontal Y component (east)).
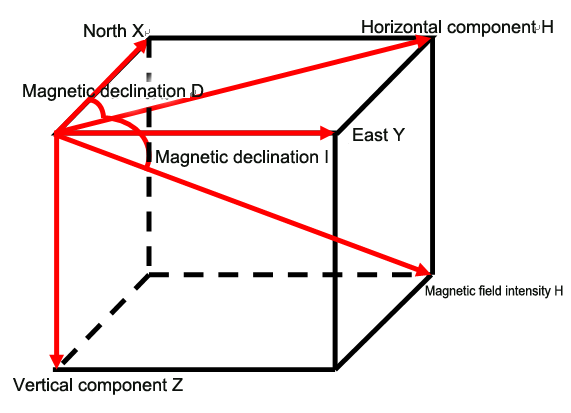
The interchanging relationship of geomagnetic elements is as follows:
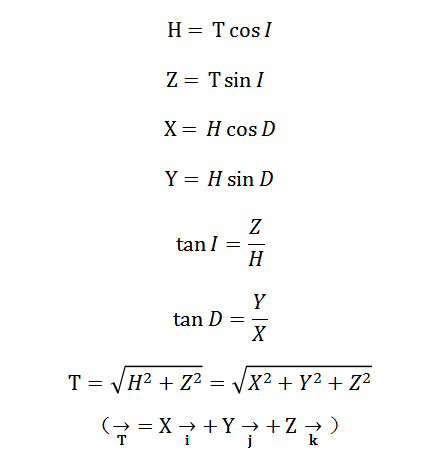
The geomagnetic field consists of basic magnetic field, changing magnetic field and magnetic anomaly. In the survey of the geomagnetic field, the magnetic field generated by the study object is called a magnetic anomaly, and the other part is called a normal field, background field or the reference field. The geomagnetic field is a vector that varies with space and time. It is associated with position and time. The geomagnetic field B observed on the earth's surface is a superposition of the magnetic field components of several sources:
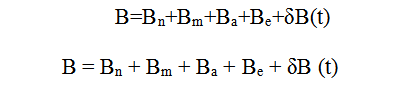
Bn-A magnetic field generated by uniform magnetization of the earth (uniform magnetic field);
Bm-A magnetic field generated by uneven magnetization inside the earth (remaining magnetic field);
Ba-A magnetic field generated by magnetization of each surface layer of the earth's crust (abnormal magnetic field);
Be-A magnetic field generated by an external cause of the earth (external magnetic field);
δB(t)-A magnetic field that varies with time (changing field).
Usually, the sum of Bn, Bm and Be is called Bo, a normal magnetic field or a basic magnetic field. Generally, as explained in the magnetic field shown in the geomagnetic chart, the sum of Bn, Bm and Ba is called Bi, an internal magnetic field. In the geomagnetic field, the internal field accounts for about 99% of the total intensity of the magnetic field, and the external field accounts for about 1%. The internal field includes the main magnetic field and the crustal field. The main magnetic field includes the dipole magnetic field and the non-dipole magnetic field, which account for 85% and 10% of the total intensity respectively. The intensity of the crustal field is basically unchanged and accounts for about 4%. The external field mainly includes the ionospheric field, magnetic layer field and induction field, which are generated by the space current system, accounting for about 1% of the total intensity. Although the geomagnetic field is mainly derived from the inside of the earth, it is shown from studies that especially the short-term variation is mainly from the outside of the earth, that is, the solar electromagnetic radiation and particle radiation (solar wind), as well as electromagnetic phenomenon such as ring current caused by the cosmic ray, etc. at the height of the earth (ionosphere and magnetosphere), resulting in high-altitude magnetic field of the earth and related geomagnetic phenomena such as magnetic storm and aurora. The magnetic storm is a strong magnetic disturbance that occurs simultaneously in the world, with the duration of about 1~3 days, and the variation range of 102~103nT. The duration of micropulsation is 1s~10min with a range of 1-10nT. The duration or period of the geomagnetic bay disturbance is 1s~10h, with the variation range of the magnetic field of 102~103nT. The period or duration of the solar diurnal variation is 24h, with the variation range of the magnetic field of 20~30nT. The period or duration of the lunar diurnal variation is 25h, with the variation range of the magnetic field of 1~2nT. The main types of variation in the internal field include non-dipole magnetic field variation, magnetic pole shift, magnetic polarity transition, main magnetic field generation mechanism and main magnetic dipole moment oscillation, etc. Generally, the variation period is long, several years to tens of thousands of years or even hundreds of millions of years. Therefore, generally, the short-term magnetic field variation mainly considers the influence of external field on geomagnetic variation. In addition, the movement of ferromagnetic objects in the earth's magnetic field causes geomagnetic variation, which is also an important factor causing variation in the external field.
2) Theory of magnetic anomaly detection
When the distance between the position of the magnetic detecting sensor and the ferromagnetic target is greater than 3 times of the target geometry, the ferromagnetic target can be simplified into a magnetic dipole model. The maximum magnetic field intensity B can be calculated by the following formula regardless of the geomagnetic background field.
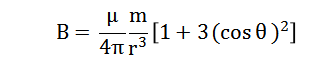
μ—Permeability;
m—Magnetic moment of magnetic doublet;
r-Distance;
Θ—Orientation.
Its magnetic field Br generated in space P is schematically shown in the following figure:

From this formula, it can be known that the magnitude of the magnetic induction intensity is related to the cubic attenuation of the distance.